As part of its traditional series of April Fool's day jokes, Google used its own .google gTLD to launch a backwards version of its home page from the domain com.google on 1st April.
However, this year's joke inadvertently undermined an important security feature on Google's real homepage, which made it vulnerable to user interface redressing attacks such as click-jacking. This vulnerability would have allowed a remote attacker to change a user's search settings, including turning off SafeSearch filters.
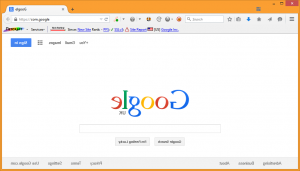
The backwards content displayed on com.google on 1 April 2015
The issue stemmed from the way com.google used an iframe to display backwards content from google.com. This would not normally be possible, as google.com uses the X-Frame-Options HTTP response header to prevent other websites from displaying itself within an iframe. But for the purpose of the April Fool's joke, Google stepped around this problem by passing the parameter "igu=2" to google.com, which not only told it to display the content backwards, but also instructed the server to omit the X-Frame-Options header entirely.

com.google used an iframe to display a backwards search page from google.com. Also note the reversed text in the HTML comment.
A remote attacker could also have leveraged this "feature" to display the Google Search Settings page in an iframe on an external domain, and trick his victims into unwittingly changing those settings. A carefully constructed clickjacking attack could have gone unnoticed by each victim until it was too late and the settings had already been changed.
To highlight the different responses, the following was an ordinary response from Google's Search Settings page at https://www.google.com/preferences?hl=en&fg=1. Note the presence of the X-Frame-Options header:
HTTP/2.0 200 OK
Alternate-Protocol: 443:quic,p=0.5
Cache-Control: private
Content-Encoding: gzip
Content-Length: 35486
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Date: Wed, 01 Apr 2015 09:54:14 GMT
Expires: Wed, 01 Apr 2015 09:54:14 GMT
Server: gws
Set-Cookie: [redacted]
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
X-Firefox-Spdy: h2-15
Conversely, with the igu=2 parameter appended, the X-Frame-Options header was omitted from the response, allowing the page to be displayed in a frame on an attacker's own website:
HTTP/2.0 200 OK
Alternate-Protocol: 443:quic,p=0.5
Cache-Control: private
Content-Encoding: gzip
Content-Length: 33936
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Date: Wed, 01 Apr 2015 09:58:30 GMT
Expires: Wed, 01 Apr 2015 09:58:30 GMT
Server: gws
Set-Cookie: [redacted]
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
X-Firefox-Spdy: h2-15
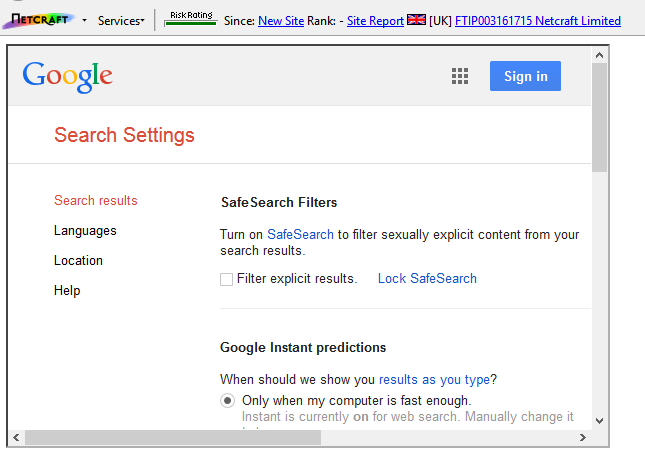
Google's Search Settings being successfully displayed within an iframe on a Netcraft domain on 1 April 2015 (this content is not served backwards).
Changes made to the above settings via the iframe would persist across the user's session when they subsequently used google.com in a normal window. Netcraft reported this issue to Google and it has since been resolved — the method described in this article can no longer be used to display the settings page within an iframe on an external domain.
Continue reading...
However, this year's joke inadvertently undermined an important security feature on Google's real homepage, which made it vulnerable to user interface redressing attacks such as click-jacking. This vulnerability would have allowed a remote attacker to change a user's search settings, including turning off SafeSearch filters.

The backwards content displayed on com.google on 1 April 2015
The issue stemmed from the way com.google used an iframe to display backwards content from google.com. This would not normally be possible, as google.com uses the X-Frame-Options HTTP response header to prevent other websites from displaying itself within an iframe. But for the purpose of the April Fool's joke, Google stepped around this problem by passing the parameter "igu=2" to google.com, which not only told it to display the content backwards, but also instructed the server to omit the X-Frame-Options header entirely.

com.google used an iframe to display a backwards search page from google.com. Also note the reversed text in the HTML comment.
A remote attacker could also have leveraged this "feature" to display the Google Search Settings page in an iframe on an external domain, and trick his victims into unwittingly changing those settings. A carefully constructed clickjacking attack could have gone unnoticed by each victim until it was too late and the settings had already been changed.
To highlight the different responses, the following was an ordinary response from Google's Search Settings page at https://www.google.com/preferences?hl=en&fg=1. Note the presence of the X-Frame-Options header:
HTTP/2.0 200 OK
Alternate-Protocol: 443:quic,p=0.5
Cache-Control: private
Content-Encoding: gzip
Content-Length: 35486
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Date: Wed, 01 Apr 2015 09:54:14 GMT
Expires: Wed, 01 Apr 2015 09:54:14 GMT
Server: gws
Set-Cookie: [redacted]
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
X-Firefox-Spdy: h2-15
Conversely, with the igu=2 parameter appended, the X-Frame-Options header was omitted from the response, allowing the page to be displayed in a frame on an attacker's own website:
HTTP/2.0 200 OK
Alternate-Protocol: 443:quic,p=0.5
Cache-Control: private
Content-Encoding: gzip
Content-Length: 33936
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Date: Wed, 01 Apr 2015 09:58:30 GMT
Expires: Wed, 01 Apr 2015 09:58:30 GMT
Server: gws
Set-Cookie: [redacted]
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
X-Firefox-Spdy: h2-15

Google's Search Settings being successfully displayed within an iframe on a Netcraft domain on 1 April 2015 (this content is not served backwards).
Changes made to the above settings via the iframe would persist across the user's session when they subsequently used google.com in a normal window. Netcraft reported this issue to Google and it has since been resolved — the method described in this article can no longer be used to display the settings page within an iframe on an external domain.
Continue reading...

